By Nwakaego Alajemba
The UK has restricted Huawei after classifying it as a high risk vendor, and has banned ZTE. The two Chinese tech companies have been accused of gathering information for the Chinese government leading to their being shut out of several countries after the US first banned Huawei in 2014 from bidding on US government contracts.
The latest ban by UK authorities could totally erase Huawei’s 5G gains in Europe and may impact negatively in less developed markets like Nigeria where it recently trialed 5G deployment.
Europe is a major market for Huawei. The UK prohibition may trigger its exit for Ericsson, Cisco, Nokia and Samsung to rule.
Huawei is the world’s leader in telecom equipment and the number two smartphone producer. When the US imposed its ban over security concerns, it asked its European allies to avoid using Huawei’s products in their 5G networks.
The Australian and French governments have ruled out Huawei and ZTE from its 5G rollout. India, next door to China, has already joined the growing list of countries shutting the door on the two Chinese technology vendors as concerns heightened that Chinese 5G equipment is embedded with spying wares.
“Overall, the UK policy will send a strong signal to the rest of Europe and the world that the use of Chinese equipment poses a security risk and should be limited. The UK and French decisions were developed to protect industries, institutions, and assets of national importance in specific geographical areas,” says UK based Strand Consult Research.
Digital Silk Road in Africa
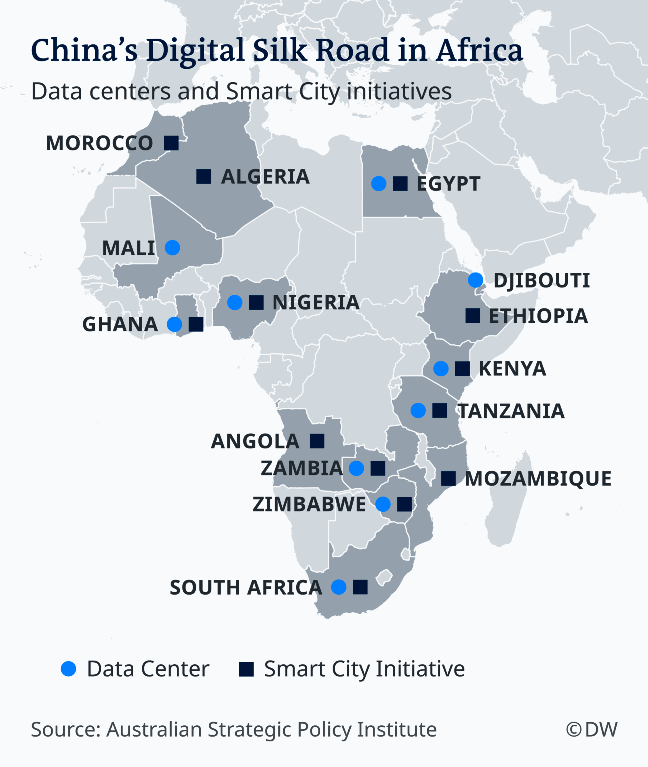
China has long ebbed out competitors in Africa’s budding technology scene and its dominance is aptly described by the German Deutsche Welle (DW) as Digital Silk Road in Africa. DW notes:
“Chinese investment in Africa’s tech infrastructure continues to gain momentum on the continent. ‘Made in China’ technology now serves as the backbone of network infrastructure in several African countries, unbeknownst to millions of users.
“Many African consumers have no idea they are using or talking on Chinese built [Internet, Communications and Technology] infrastructure,” says Iginio Gagliardone, a professor at the University of the Witwatersrand in South Africa.
“Chinese firms like Huawei, ZTE and China Telecom are behind the core systems of new ICT infrastructure across Africa. And they are providing the next generation of technology.” The report is titled: ‘Investing in Africa’s tech infrastructure. Has China won already?’
From Algeria, Mali, Ghana, Tanzania to Zambia, Ethiopia, Angola, Uganda, South Africa, Kenya, Nigeria and Zimbabwe the two Chinese giants have rolled out over 50 third-generation (3G) telecoms networks in more than 36 African countries. They lead Africa’s 4G rollout and are spearheading the 5G buildout. All of these with the backing of Beijing, note a report by The East African.
But China has been accused of promoting state-sponsored espionage in all of its projects across the continent. Its gift of an African Union (AU) Headquarters building in Addis Abba was allegedly bugged to allow the Chinese eavesdrop on the 55 African countries that make up the AU. China has denied this even as allegations heightened that its two vendors are spy machines for Beijing.
With the recent UK’s decision, Africa countries mostly colonised by European powers may finally shut their doors on China “if they will offer affordable options as does China,” one commentator in Abuja would say.
But for now, Nigeria, a major market for Huawei and ZTE on the continent, appears not to be looking at interrogating or ending its romance with the Chinese vendors.
UK new policy restricting Huawei and banning ZTE is a step in the right direction, says Strand Consult Research
Much has been written about the decision the UK government made today regarding the use of Chinese-made equipment from Huawei in UK mobile networks.
This research note offers Strand Consult’s assessment based upon in-depth policy analysis, interviews, and other intelligence on this issue since 2005.
- The decision relates to the use of Huawei equipment in the United Kingdom. In practice, this means that the May 2018 total ban on ZTE equipment by the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre will continue.
- Huawei are now classified as a high risk vendor following the conclusions of the Telecoms Supply Chain Review.
- The use of Huawei equipment will be prohibited in core networks. This means that the backbone of UK mobile networks must not contain Huawei equipment. This policy demonstrates that UK authorities recognize the risk of equipment made by entities affiliated with the Chinese government. If Chinese-made equipment was safe, Huawei equipment would not be prohibited from the network core.
- The use of Huawei in the radio access network (RAN) will be limited to 35 percent of the active equipment. This limits the amount that Huawei can sell in the UK. It also means that UK operators will have to prioritize network upgrades in the Western part of the country where Huawei equipment is largely deployed. In practical terms, it will not be possible for an operator to use Huawei for more than 35 percent of the equipment and then use another Chinese or Huawei-white labeled product for the rest of the network, or a portion thereof. The goal of the policy is to limit equipment from Chinese owned and/or affiliated entities, even if it is not explicitly written.
- The use of Huawei equipment will be expressly prohibited in sensitive geographical areas in the UK, areas selected for national security reasons. Indeed, this is already practiced in France where Huawei equipment in restricted in Toulouse, home of Airbus and the European aerospace industry. A similar policy exists for Brest where French nuclear submarines are located. Read more about the French decision.
Overall,
the UK policy will send a strong signal to the rest of Europe and the world
that the use of Chinese equipment poses a security risk and should be limited.
The UK and French decisions were developed to protect industries, institutions,
and assets of national importance in specific geographical areas.
The US model restricts its military from using Huawei and ZTE, regardless
of location. Moreover, the Federal Communications Commission prohibits the use
of its subsidies for the purchase of Huawei and ZTE equipment and is
considering the requirement of removal of Huawei equipment for future
subsidies.
Additional US policy restricts American firms from transacting business
with Huawei for sensitive technologies. US telecom operators, noting the risk,
have largely opted not for Huawei or ZTE, outside of a few exceptions. This is
explained in Strand Consult’s research note The pressure to restrict Huawei
from telecom networks is not driven by governments, but the many companies that
have experienced hacking, IP theft, or espionage.
The UK new policy is a step in the right direction, and it underscores
the need for greater scrutiny of technology from firms owned and/or affiliated
with the Chinese government. The security risks are real and networks are key
vulnerability. Indeed, scrutiny should extend beyond the network equipment to
other vulnerable products and services; systems can be compromised by devices
attached to networks as well as from software running over it. See Strand
Consult’s research note “The debate about network security
is more complex than Huawei. Look at Lenovo laptops and servers and the many
other devices connected to the internet.”
Strand Consult expects that the security standards required for public
safety networks will be strengthened and translated to commercial telecom
networks. It is likely that some UK operators will claim that the new policy
will be unduly expensive. Strand Consult examines such claims in the
report ”The real cost to rip and replace
Chinese equipment from telecom networks.”
Notably 2G / 3G / 4G equipment must be replaced anyway in the move toward
5G. Huawei is not the only vendor, and alternatives are price competitive.
Moreover, when it comes to 5G, network rollout policy is far more consequential
than the choice of equipment vendor. The view that Huawei is necessary for 5G
is a myth; indeed, the US has taken a leadership position on 5G without using
Huawei equipment.
Looking at the historical facts, it is not difficult to find operators
which have swapped their networks with a new supplier. This need not come as a
premium for shareholders. Strand Consult reviews the financial data and case studies
from the major network swap it observed in 2010 – 2016.
The UK government, with Boris Johnson at the forefront, can improve the
prospects for 5G in a meaningful way. In the UK, as in many other countries, it
is both difficult and expensive to build mobile infrastructure. Strand
Consult’s analysis show that the terms and costs associated with obtaining
permits and leasing land for mobile masts and towers is artificially expensive.
In the UK, operators have for many years and with limited success tried to
change the terms.
In Denmark, on the other hand, Strand Consult has helped to create
transparency so that authorities get the information they need to create the
needed rollout policies. As a result, the total rental costs for mobile
operators have fallen by over 20 percent, and it has become significantly
cheaper and easier to upgrade and build existing and new mobile infrastructure.
Learn more about the project here ”How to deploy 5G: Best practices
for infrastructure, regulation and business models.”
Conclusion
Huawei will likely claim that the UK decision doesn’t hurt its prospects. This
is probably to save face. The fact is that Huawei will be subject to increased
restriction and will not be able to enlarge its market share. Moreover, there
is no change on the ZTE ban. The UK makes clear that Chinese equipment is not
allowed in the core network. Moreover, when it comes to RAN, there are also
strict limitations.
Other report sources
Deutsche Welle (DW): https://www.dw.com/en/investing-in-africas-tech-infrastructure-has-china-won-already/a-48540426
The East African: https://www.theeastafrican.co.ke/business/Africa-embraces-Huawei-despite-security-concerns/2560-4908166-15t6impz/index.html
Aljazeera: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2018/12/countries-banning-huawei-181206130850129.html
The Verge: https://www.theverge.com/2018/1/29/16946802/china-african-union-spying-hq-cybersecurity-computers-backdoors-espionage
































