$5,600 lost every single minute. That’s how much the average data center sacrifices during moments of downtime, a relentless drain on resources that sends shockwaves through entire organizations. Each minute offline doesn’t just mean lost revenue; it signifies a breach of trust, a disruption in service, and potential chaos for those relying on these vital infrastructures. As cybercriminals become increasingly cunning, the threat landscape surrounding data centers grows more perilous, endangering sensitive data and the very foundation of digital commerce.
RELATED: Finding lost smiles: How facial recognition brings children back to their families
In this high-stakes environment, securing data centers is not just about protecting assets—it’s about safeguarding livelihoods and maintaining the trust of clients. While physical stability remains the top priority—ensuring an uninterrupted power supply, protecting against environmental threats, and securing communication channels—the importance of addressing digital threats cannot be underestimated. Physical threats, although often considered secondary, can be just as critical, as many of these risks stem from human actions. This highlights the need for a comprehensive security system that goes beyond traditional measures, ensuring that data centers stay resilient, secure, and capable of responding to both physical and digital threats. In a world of increasingly sophisticated attacks, prioritizing robust, proactive security systems is essential to maintaining continuous, reliable service and protecting sensitive data.
Unraveling the Data Center Threat Landscape
Data centers face constant and evolving threats, with attackers targeting both physical infrastructure and digital assets. According to the 2022 Official Cybercrime Report, cybercrime costs are projected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025, and the cost of individual breaches is rising sharply to $9.48 million in 2023 alone. These alarming figures underscore the complexity of the security landscape, posing significant challenges that encompass both physical and cybersecurity threats.
Ransomware attacks, in which hackers encrypt important data and demand money to unlock it, have become a serious worry. These assaults can result in significant financial losses, data loss, and long-term damage to one’s reputation. These attacks have recently had a greater financial impact; the average ransom payment increased from $812,380 in 2022 to $1,542,333 in 2023. Similarly, phishing assaults have become one of the fastest-growing cyberthreats, with a 58% increase in only the past year. As of 2024, the expected global financial cost of phishing, including both direct losses and recovery expenses, is $3.5 billion. These numbers highlight how important it is for businesses to be alert and modify their security plans in order to handle the growing complexity and severity of contemporary cyberthreats.
While technology plays a critical role, it cannot fully prevent security breaches, as human error and insider threats continue to pose significant risks. Even with robust measures, accidental actions can compromise sensitive data and erode trust. Additionally, standard access controls may be insufficient, leaving physical infrastructure vulnerable.
The need for complete control from entry to exit is paramount. Data centers must implement strict physical security measures and simultaneously handle cybersecurity threats originating from privileged users who may purposefully or unintentionally abuse their access. Integrating information and physical security is crucial for a comprehensive strategy for asset protection. Vulnerabilities in identity verification also add another level of danger; if authentication procedures are too difficult, users might look for workarounds that leave the system vulnerable.
Remote channel access control is still an issue because traditional authorization techniques can be hacked, giving bad actors the opportunity to take advantage of system flaws. Accurately tracking and logging actions can be challenging when security measures lack personalization, which can impede effective access management. Monitoring customized actions and improving overall security posture need the integration of enhanced logging features into Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Physical Security Information Management (PSIM) systems.
As data centers continue to evolve, addressing these multifaceted security challenges will be vital to ensuring their resilience against an ever-changing threat landscape. By recognizing and mitigating risks, data centers can protect their vital infrastructure and the businesses that rely on them.
How Facial Recognition Systems (FRS) Stand Guard
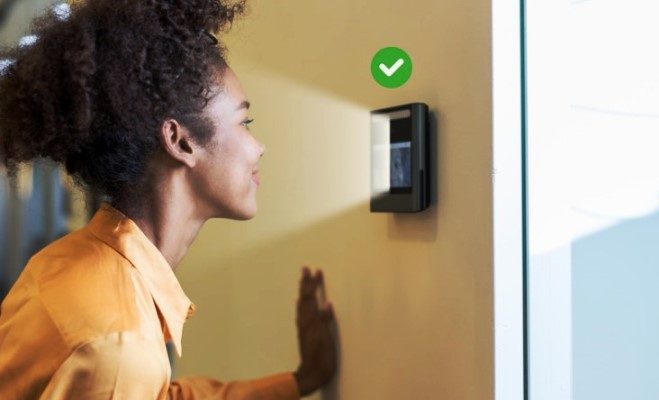
One promising solution to enhance security is the implementation of Facial Recognition Systems (FRS). As these facilities confront an evolving landscape of threats, FRS emerges as a powerful ally in strengthening both physical and digital defenses.
By leveraging advanced biometric technology, FRS enhances access control, surveillance, and remote authentication, creating a comprehensive security framework tailored to the unique needs of data centers.
Enhanced Access Control
The core of FRS is its capacity to guarantee accurate entry and exit verification, allowing only authorized personnel to enter. By thoroughly recording every activity, this careful management not only protects sensitive regions but also promotes accountability. By distinguishing between actual people and photos, liveness detection technology provides an additional degree of protection and successfully prevents identity spoofing attempts. Furthermore, the system’s capacity to immediately notify security professionals of any illegal access attempts enables them to react to possible threats in a timely and efficient manner.
Robust Surveillance Capabilities
By continuously authenticating people within secure zones, FRS greatly improves data center surveillance. This continuous verification process aids in identifying unwanted behaviors, such as attempts to view sensitive information, that could otherwise go undetected. Data centers can implement such a solution on their own, or they can delegate the task of physical security control to a specialized agency. The entire security posture is improved by automatically identifying and documenting suspicious activity in Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Physical Security Information Management (PSIM) systems. This ensures that all occurrences are logged for review and action. Looking into the future, the same security agency can expand the range of its services and increase the efficiency of protection and speed of response to incidents through facial recognition technology.
Cyber Access Control
By substituting biometric authentication for traditional password systems, FRS provides a strong cybersecurity alternative. This change not only lowers the risk of credential theft but also introduces continuous user verification throughout sessions, which greatly lowers the possibility of session hijacking. In addition to identifying possible hazards like unwanted observers trying to access private information, advanced fraud detection techniques also provide instant warnings so that IT teams may respond quickly to any instances that are reported.
Streamlined Remote Access
FRS plays a vital role in ensuring remote access as remote work becomes more common. The system makes sure that only authorized workers can interact with sensitive data and important systems by accurately verifying remote users’ identities. This security layer is further strengthened by liveness detection technology, which can automatically stop access if a compromise is suspected. Instant notifications and detailed incident logs in SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and PSIM (Physical Security Information Management) allow security teams to swiftly address any security concerns, ensuring the integrity of remote operations.
Physical access, digital safety, and remote authentication are all covered by the layered, responsive, and proactive approach to security that organizations can adopt by integrating FRS into their data center’s security framework. This strong implementation not only improves security but also strengthens the resilience and integrity of data centers, guaranteeing their security in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
What’s Next for FRS in Data Center Security?
Facial Recognition Systems (FRS) are rapidly evolving, becoming essential tools in data center security. Key advancements include the ability to monitor multiple entry points from a single platform, enhancing operational efficiency. Facial biometrics serve as a bridge between physical, digital, and cyber security. Additionally, ready-made software solutions are simplifying deployment, as these pre-configured tools integrate seamlessly with existing data center systems. Innovations in age progression and regression enable FRS to recognize individuals even as their appearances change, ensuring long-term reliability in environments with long-term access.
Modern FRS are also addressing the challenges of bias, utilizing machine learning and AI to accurately recognize individuals across diverse populations, regardless of race, gender, or ethnicity. Enhanced features like anti-spoofing and liveness detection further strengthen security by preventing unauthorized access attempts through photos or masks. Beyond data centers, FRS is transforming various sectors, including healthcare for secure patient identification, smart cities for public safety, and banking for financial inclusion. The future of FRS is promising, with ongoing improvements poised to tackle the evolving security challenges of the digital age.
Building Resilience for Tomorrow’s Data Centers
To effectively address modern security threats, data centers must adopt a comprehensive approach that integrates advanced technologies like Facial Recognition Systems (FRS) with robust physical and cybersecurity measures. However, the integration of this technology raises privacy concerns that organizations must manage. Data centers should maintain transparency about how biometric data is collected, stored, and utilized while implementing stringent data protection policies to safeguard against breaches.
As we navigate the ever-changing digital frontier, data centers must face evolving threats with a commitment to innovation in security strategies. Each technological advancement contributes to a more secure future, but it’s crucial to foster a culture of awareness among staff. When every team member understands the importance of robust security practices, they become the first line of defense. Together, we can ensure that data centers remain fortified strongholds against emerging threats, safeguarding not only the assets within but also the trust of clients and communities. Striking a balance between cutting-edge solutions and strong security measures is vital. This approach not only protects our digital assets but also builds a safer, more trustworthy world.
“Facial recognition transforms data center security into a proactive defense, seamlessly integrating with cybersecurity protocols to shield critical assets. It’s more than just technology—it’s the silent guardian that fortifies trust, resilience, and continuity in today’s volatile threat landscape,” said Oleg Kurochkin, Business Development Director, APAC region, RecFaces.
Want to know more? Click to register for our webinar.