One of Nigeria’s major mobile network operators (MNOs) has allegedly been hacked. The attackers have gained foothold of parts of valuable data and infrastructure of the telco for over a week now significantly incapacitating it from delivering many essential services. According to a story trending online, the hackers want $2.5 million ransom payment before they can release parts of the network now under their control.
The telcos are not talking. But industry persons familiar with the matter have confirmed the hack to IT Edge News.Africa and said the company is trying to manage the crisis without suffering an additional public image dent which could impact on its profit.
Attack is said to involve Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) and Network Intrusions.
“Software developers in Nigeria are good with brilliant ingenious solutions for easy and speedy payment which organisations like because you want to take money off customers quickly but these developers in Naija [Nigeria]do not give indepth considerations to security during the development phase,” said one expert with knowledge of the Nigerian industry.
Worldwide, telecom companies are frequently targeted by various cybersecurity attacks. “But this current attack is super-revealing of just how unprepared most Nigerian MNOs are. There is a worrying cosmetic approach to hardcore cybersecurity issues,” the source added.
Twitter on fire
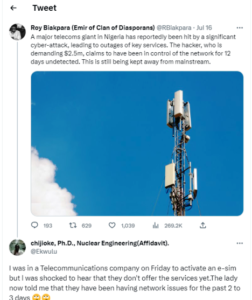
Roy Biakpara (Emir of Clan of Diasporans) @RBiakpara tweeted: “A major telecoms giant in Nigeria has reportedly been hit by a significant cyber-attack, leading to outages of key services. The hacker, who is demanding $2.5m, claims to have been in control of the network for 12 days undetected. This is still being kept away from mainstream.
“The sources don’t want the identity of the telecoms company to be revealed yet. This latest incident demonstrates the continued threat posed by cyberattacks where many Nigerian companies invest in paper security certifications rather than proper security controls.
“Based on the information gathered so far, it appears that the company in question does not allocate much of its budget towards recruitment efforts. This potentially indicates a strong reputation in the industry, attracting top talent through word of mouth or “other methods.
“Most Naija companies rely heavily on referrals to fill vacancies. Regardless of the reason, it’s important to adjust their recruitment strategies to ensure that they are able to attract qualified cybersecurity candidates for situations like this.
“A Zoom incident response meeting is currently underway.”
Also, chijiоke, Ph.D., Nuclear Engineering(Affidavit) @Ekwulu tweeted: “I was in a Telecommunications company on Friday to activate an e-sim but l was shocked to hear that they don’t offer the services yet. The lady now told me that they have been having network.”
Inherent nightmares operators must live with
Telecom operators frequently implement security measures, including network monitoring, regular software updates, employee training, strong access controls, and incident response plans among others. But cyberattaks have become inherent nightmares operators must live with.
Here are some likely cybersecurity attacks that telecoms companies may face:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks involve overwhelming a network or website with a flood of traffic, causing it to become unavailable. Telecoms companies are often targeted with DDoS attacks to disrupt their services or extort money.
- Network Intrusions: Cybercriminals may attempt to gain unauthorized access to telecom networks to steal sensitive information, manipulate call records, intercept communications, or disrupt services. This can be achieved through techniques like exploiting software vulnerabilities, password cracking, or social engineering.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are sophisticated, targeted attacks that involve long-term intrusion into a network. APT actors, often state-sponsored, employ various techniques to gain unauthorized access and persistently monitor and exfiltrate data over an extended period. Telecoms companies may be targeted due to their role in critical communications infrastructure.
- Phishing and Spear Phishing: Phishing attacks involve tricking individuals into divulging sensitive information or credentials by posing as a trustworthy entity. Spear phishing is a more targeted form of phishing, where attackers customize their messages to appear as if they come from a known contact or trusted organization. Telecoms employees may be targeted to gain access to internal systems or user data.
- Malware Attacks: Telecoms networks may be infected with malware, including viruses, worms, or ransomware. Malware can be spread through malicious attachments, infected websites, or software vulnerabilities. Once inside the network, it can disrupt operations, steal data, or encrypt files for ransom.
- Insider Threats: Employees with authorized access can pose a significant cybersecurity risk. Insiders may intentionally leak sensitive information, sabotage systems, or abuse their privileges for personal gain. Effective access controls and monitoring systems are crucial for mitigating insider threats.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Telecom companies often rely on third-party vendors for hardware, software, or services. Cybercriminals may compromise these suppliers to gain unauthorized access to the telecoms’ network, install backdoors, or tamper with equipment. This can result in data breaches or system compromises.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals through psychological tactics to gain access to confidential information. Attackers may impersonate employees, customers, or authorities to deceive telecoms company personnel into revealing sensitive data or providing unauthorized access.
































