Kaspersky’s Digital Footprint Intelligence team studied the darknet job market. After analysing 200,000 employment ads between 2020-2022, the experts found that developers, attackers and designers were the most sought after professions in the cybercriminal community. Based on Digital Footprint Intelligence, job requirements included creating malware and phishing pages, compromising corporate infrastructure, hacking web and mobile applications, and other responsibilities. The median levels of pay offered to IT professionals varied between $1,300 and $4,000 per month.
RELATED: Cybercriminals sell access to companies via the Dark Web from $2000
The Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence (DFI) team reviewed job ads and resumes posted on 155 dark web forums between January 2020 and June 2022, analysing those containing information about long-term or full-time jobs. According to DFI service data, a total of roughly 200,000 employment-related ads were posted on the dark web during the period analysed. Forty-one percent of ads were posted in 2020, with activity peaking in March – possibly because of a pandemic-related income drop experienced by part of the population.
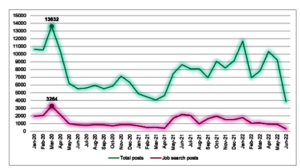
Monthly posting dynamics for ads seeking and offering jobs on dark web job forums in 2020–2022
Kaspersky experts analysed IT jobs and selected more than 160 of the ones that explicitly cited a salary, although dark web employers typically state rough salary figures¹. The median levels of pay offered to IT professionals varied between $1,300 and $4,000 monthly. The highest median salary of $4,000 could be found in ads for reverse engineers.
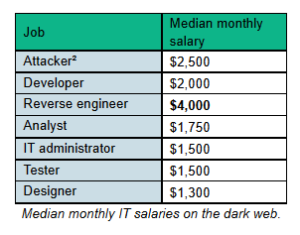
The highest monthly salary Kaspersky experts saw in the ads was $20,000 – awarded to a developer. The lowest fee offered was just $200. Some dark web job ads included bonuses and commissions from successful projects, such as extorting a ransom from a compromised organisation.
Developers, attackers and designers topped the list of the most demanded dark web jobs
Developers were the most in-demand specialists on the dark web: this specialty accounted for 61% of all ads. Within this specialty, web developers, who create various Internet products like phishing pages, was most sought after accounting for 60% of these ads. Also valued were malware coders. This job description can include development of Trojans, ransomware, stealers, backdoors, botnets, and other types of malware, along with the creation and modification of attack tools.
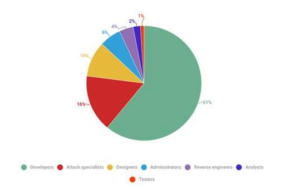
Distribution of dark web job ads across specialisations.
Attackers – or IT specialists who conduct attacks on networks, web applications and mobile devices – were the second most popular jobs among cybercriminal employers, accounting for 16% of the total ads. The closest approximation to a legitimate profession of this job is penetration tester. Most of the attackers’ jobs on the dark web were associated with actions that would compromise corporate infrastructure. The goals of these actions are ransomware infection, data theft, or stealing cash directly from accounts. Some cybercriminal groups hiring attackers were focused on selling access to compromised systems to other cybercriminals, or hacking web and mobile applications.
Designers were the third most professionals in demand with 10% of ads. Their goal usually is to make a malicious product, such as a phishing page or letter that would be hard to distinguish from the real one.
Darknet employers also look for IT administrators, reverse engineers, analysts, testers and other less common IT jobs – various kinds of engineers and architects, support specialists, technical writers, forum moderators, and even executives and project managers.
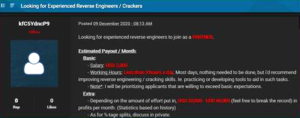
Example of a job ad for a reverse engineer.
“IT headhunting is one of the numerous topics which is constantly discussed on the Darknet. Nowadays, tracking cybercriminal’s interest and continuous analysis of their activities is vital for companies that want to proactively respond to cyberattacks and keep their information security at the highest level. The more you know about your adversary – the better you are prepared,” said Polina Bochkareva, Security Services Analyst at Kaspersky.
To learn more insights about dark web job market please visit Securelist.com.
To protect from threats targeting business, Kaspersky researchers recommend implementing the following measures:
- Continuous monitoring of Dark web resources significantly improves the coverage of various sources of potential threats, and allows customers to track threat actor’s plans and trends in their activities. This type of monitoring is a part of Kaspersky’s Digital Footprint Intelligence service.
- Use the multiple sources of Threat Intelligence information (with coverage of surface, deep and dark web resources) to stay aware of actual TTPs used by threat actors.
- Dedicated services can help combat high-profile attacks. The Kaspersky Managed Detection and Response service can help identify and stop intrusions in their early stages, before the perpetrators achieve their goals. If you encounter an incident, the Kaspersky Incident Response service will help you respond and minimise the consequences. For example, it can identify compromised nodes and protect the infrastructure from similar attacks in the future.
References:
¹ Salary levels expressed in Russian rubles were converted using the effective rate at the time of the study: 75 rubles per dollar.
² IT specialists who conduct attacks on networks, web applications and mobile devices.































