Key findings:
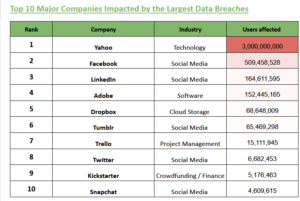
- Yahoo’s 2013 breach was the largest data leak among well-known companies, with 3 billion users affected
- Half of the top 10 companies affected by data breaches are in the social media industry
- Email addresses are the most commonly exposed information in data breaches, appearing in 20.75% of leaks
In 2024, the average cost of a data leak soared to USD 4.88 million (£3.6 million). However, businesses that implemented security AI and automation extensively managed to save an impressive $2.22 million (£1.6 million) in prevention costs. 1
RELATED: Massive data breach hits BestFin Nigeria: 846,000 customers’ data exposed
Recognising the significant financial impact of data breaches, the experts at application security SaaS company Indusface set out to identify the biggest data leaks among large, recognisable companies.
To accomplish this, they analysed the number of users affected and monitored changes in search interest in the years following each breach.
Top 10 Major Companies Impacted by the Largest Data Breaches
Please see the full data here
Yahoo’s 2013 breach largest among major companies analysed
Indusface reports that Yahoo’s 2013 breach was the largest among major companies analysed, affecting 3 billion users. Despite this, the breach wasn’t made public until September 2016, leading to a 9.52% drop in search interest from that year.
Yahoo faced a $35 million (£26 million) fine from the SEC for failing to disclose the breach properly and paid a $117.5 million (£89 million) settlement. Investigations by the Irish Data Protection Commissioner and the FBI followed, with the FBI indicting four individuals, including two suspected FSB spies. The breach also heightened public awareness of cybersecurity laws and regulations.
Facebook experienced the second largest data breach of companies analysed, impacting 509,458,528 users. Notably, three years after the breach, search interest following the incident dropped by 33.96%.
In April 2021, over 500 million users’ information was made freely available for download, representing approximately 20% of the platform’s subscribers. This data was allegedly obtained by exploiting a vulnerability that Facebook claimed to have fixed in August 2019. While every record included a phone number, 2.5 million also contained an email address. In third place is LinkedIn, with 164,611,595 users affected by a breach that occurred in May 2016. Interestingly, despite this breach, LinkedIn saw a 39.49% increase in search interest. During the incident, 164 million email addresses and passwords were exposed. Although LinkedIn was originally hacked in 2012, the compromised data remained hidden until it was offered for sale on a dark market site four years later. The passwords were stored as SHA-1 hashes without salt, allowing the vast majority of them to be easily cracked within days of the data’s release.
Snapchat ranks tenth with its 2014 data breach, which affected 4,609,615 users. Surprisingly, search interest for the platform surged by 312% just three years after the incident, suggesting the leak had little impact on its overall appeal—likely because Snapchat had yet to hit its peak popularity.
Must-know tips to shield your business from data leaks
Venky Sundar, Founder and President of Indusface, shares must-know tips to shield your business from data leaks and breaches:
- Encrypt sensitive data: Ensure that all sensitive data, both in transit and at rest, is encrypted to prevent unauthorised access.
- Implement strong access controls: Limit access to sensitive information based on roles and enforce multi-factor authentication for added security.
- Regularly update software: Keep operating systems, applications, and security tools updated to patch vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches. If a software update breaks systems, deploy virtual patches on the web application firewall as an emergency measure. After that you could prioritize software updates in later dev cycles.
- Conduct employee training: Educate employees on data security best practices, phishing threats, and the importance of handling sensitive information properly.
- Monitor network activity: Use intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic and alert you of any suspicious activity.
- Backup data regularly: Maintain secure, encrypted backups of critical data to minimise damage in the event of a breach or ransomware attack.
- Enforce strong password policies: Require complex passwords and regular updates to reduce the risk of unauthorised access.
- Conduct regular security audits: Perform internal and external audits to identify and address any security gaps or vulnerabilities in your systems.
- Monitor zero-day threats: Every month hundreds of new SQLi vulnerabilities are found. Monitor these and deploy the patches. If patching needs to be delayed, deploy application specific virtual patches on the WAF layer.
- Create a mobile device action plan: To safeguard sensitive data on mobiles, require users to set strong passwords, encrypt data, and install security apps. Additionally, implement clear reporting procedures for lost or stolen devices.
- Secure Wi-Fi networks: Ensure your workplace Wi-Fi is secure, encrypted, and hidden. Disable SSID broadcasting and password-protect the router for added security.
Methodology
- Indusface set out to explore how major data leaks from large, well-known companies impacted their reputations.
- To do this, we first compiled a list of data breaches from haveibeenpwned.com, focusing only on recognisable brands. We chose larger companies because their changes are easier to track compared to smaller, more niche sites. For completeness, we manually added some major breaches, like Yahoo’s 2013 breach, which wasn’t publicly disclosed until 2016.
- Next, we used Google Trends to measure the popularity of each brand before and after the breach. Specifically, we compared the average search trends from the year leading up to the breach with the trends 1, 2, and 3 years afterward to see if there was any significant drop.
- We also noted how each company responded to their breach—especially if their actions went beyond standard security updates. This was recorded under the “Breach Response” section.
- For publicly traded companies, we tracked their stock performance around the time of the breach. We compared their average stock prices in the year before the breach to 1, 2, and 3 years afterward. Additionally, we looked at their stock prices the day before the breach and then 1, 2, and 3 days after, to check for any immediate impact. All stock prices are listed in USD.
- Please note, the trend data after the breach may not be entirely due to the breach itself—many factors can influence a company’s relevance. This data is meant to give a broad, anecdotal view. Also, some breaches occurred before a company became a major player, like in the cases of Epic Games and Snapchat.
- You can view the full data here.
- Data accurate as of September 19th.





























