In an era when digital technology intertwines with everyday life, the healthcare sector stands at the forefront of adopting innovative solutions to safeguard sensitive information. Among these technologies, facial recognition emerges as a vital tool against data breaches and identity theft.
RELATED: Face value: The ethics of facial recognition biometrics
As World Health Day draws near, it’s crucial to highlight the significance of facial recognition in the health industry and to observe what challenges it helps to overcome.
Statistics
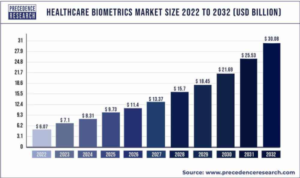
The global healthcare biometrics market is on a remarkable ascent. With an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18% between 2023 and 2032, the sector is rapidly acknowledging the indispensability of biometric verification in enhancing healthcare security. This growth is not only a reflection of technological advancement but also an indicator of the growing need for people to protect themselves both physically and digitally.
Statistics show that the number of data breaches in the medical field has risen dramatically over the years. In 2023, healthcare data leaks involving 500 or more records were reported every day on average (1.99 incidents per day). Approximately 364,571 medical records were compromised every day.
Identity theft
Medical identity theft, where individuals’ personal health information is stolen to receive medical services, prescription medications, or surgery, jeopardizes both the financial stability of victims and the credibility of healthcare providers. The consequences extend beyond monetary loss, encompassing incorrect entries in medical records, which can lead to inappropriate treatment and misdiagnosis. Moreover, identity theft usually results in granting access to sensitive areas within medical facilities. As such incidents occur, the need for robust security measures in the healthcare industry becomes increasingly important.
Solutions
Facial recognition technology emerges as one of the most promising solutions to address multiple challenges faced by the health sector:
- Access control. Sensitive areas within healthcare facilities, such as operating rooms, pharmacies, and patient records archives, can be safeguarded against unauthorized entry. While ID cards and badges can be stolen or shared with third parties, facial features are unique, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to the critical areas, minimizing the risk of data breaches and theft. In addition, facial recognition solutions can perform Liveness checks that help to ensure that there is a real person in front of the terminal. For example, RecFaces’ solution Id-Gate only needs a moment to determine that the face presented is a live human being and not the photo.
Example: Medical facility workers do not need to spend time searching for a pass to gain access to restricted areas, which allows them to instantly be at the required spot. This is extremely important in emergency situations, when every second matters.
- Maintenance of patient accounts. By integrating facial recognition into electronic health record systems, healthcare providers can ensure accurate patient identification and streamline administrative tasks, from updating medical histories to verifying insurance information.
Example: A hospital implements a facial recognition system at registration desks. Upon arrival, a patient’s face is scanned, and their medical records are automatically retrieved from the hospital database. This minimizes human identification errors and expedites the check-in procedure, eliminating the issue of queues and patients being late for appointments.
- Enhanced patient experience. Patient check-in processes can be time-consuming, which frequently leads to long wait times and inefficiencies. Facial recognition simplifies this procedure by swiftly identifying patients upon arrival, eliminating the need for manual verification and paperwork. RecFaces’ solutions, for instance, perform identity checks in less than a second, preventing queues and lengthy wait times. This not only enhances patient satisfaction but also optimizes staff resources and improves overall operational flow.
Example: In a clinic, when patients arrive for their appointments, they simply approach the terminal, where a camera captures their facial image. The facial recognition system then matches the captured image with the patient’s pre-registered profile in the hospital’s database. Once the patient’s identity is confirmed, they are automatically checked in for their appointment without the need for manual paperwork or staff intervention.
- Medical data safety. Threats of medical data theft remain prevalent, with cybercriminals targeting healthcare organizations to exploit valuable patient information for financial gain or identity theft. From ransomware attacks to insider threats, the consequences of medical data breaches can be severe, resulting in compromised patient privacy, financial losses, and an illegal drug trade. By accurately verifying the identity of users logging into healthcare systems, facial recognition mitigates the risk of unauthorized access and stops criminals from taking advantage of stolen data.
Example: A research laboratory storing sensitive medical data and experimental medications employs facial recognition technology at entry points. Only authorized personnel whose faces are registered in the system can access the facility, ensuring data security and preventing theft or mishandling of valuable resources.
- Telemedicine consultations. Facial recognition technology plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and efficiency of virtual consultations. By authenticating the identity before each session, these systems safeguard patient confidentiality and ensure that the individual utilizing the telemedicine platform is, in fact, a registered patient.
Example: There is no need to look for documents and spend time on the road to the medical institution. One glance at the camera of a device is enough to start the consultation, which can be especially convenient if the patient is not feeling well. At the same time, both the doctor and the patient can be confident that they are talking to the person with whom the consultation was scheduled.
- Pandemic management. Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare facilities introduced facial recognition systems with thermal scanning at entry points to monitor visitors and employees for elevated body temperatures. Since then, the versatility of such systems has expanded significantly. Now, these systems effectively conduct facial recognition even when individuals are wearing medical masks, while contactless identification supports ongoing hygiene measures in medical institutions beyond the global pandemic.
Example: Healthcare facilities integrate thermal scanning systems with facial recognition at entrances to screen patients, visitors, and staff for elevated body temperatures. Such systems not only help to identify visitors but also make sure that individuals with potential symptoms are flagged for further evaluation.
In a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape where the safeguarding of confidential information is paramount, facial recognition promises a future where safety, efficiency, and patient-centered care converge seamlessly. Let us celebrate this World Health Day by championing the development of facial recognition technology and paving the way for a healthier, more secure tomorrow.